Collection Tools Component
Common collection operations
Component key: collection-tools
Description
The collection tools component contains actions that let you perform common tasks on collections of data (objects and arrays). You can do things like concatenate objects, filter items of lists (arrays), map functions on items, and more.
We use the terms list and array interchangably on this page. Both describe a set of objects. Similarly, the terms items and elements of a list are used interchangably.
The functions that you provide these actions for filtering, mapping, etc., should be NodeJS functions. Examples are below.
Actions
Add Key/Value to Object
Add a value to an object with the given key | key: addKey
| Input | Notes | Example |
|---|---|---|
Key string / Required key | My Comments | FirstName |
Object code / Required object | ||
Insert Path string objectPath | Optionally define a path using dot notation of where to add the key/value | employee.contact |
Value string / Required value | Jake |
If you would like to insert a key/value pair into a nested portion of the object, use the Insert Path input to specify where it should be added. For example, if your object reads:
{
"employee": {
"id": "123",
"hired": "2022-03-05T00:08:00",
"contact": {
"phone": "6024441234"
}
}
}
You can add an email address to contact by specifying "email" for Key, "example@company.com" for Value, and employee.contact for Insert Path.
The result will be:
{
"employee": {
"id": "123",
"hired": "2022-03-05T00:08:00",
"contact": {
"phone": "6024441234",
"email": "example@company.com"
}
}
}
Example Payload for Add Key/Value to Object
{
"data": {
"employee": {
"id": "123",
"hired": "2022-03-05T00:08:00",
"contact": {
"phone": "6024441234",
"FirstName": "Jake"
}
}
}
}
Aggregate
Apply aggregate function to list | key: aggregate
| Input | Default | Notes | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
Aggregate Function string / Required aggregateFunctionInput | Aggregate function to apply (choose from AVERAGE, COUNT, MAX, MIN, SUM, PRODUCT, MEDIAN). | SUM | |
Filter Function code filterCodeInput | Filter out any elements that do not return true | ||
List code / Required listInput | Reference to a list of data to operate on |
This action applies the filter function (if given) first, and then applies the aggregate function to the filtered list. See the Filter action for examples of how to use the filter function.
Example Payload for Aggregate
{
"data": 117
}
Append
Append element to the end of the list | key: append
| Input | Notes |
|---|---|
Element data / Required elementInput | The item to append to the end of the list |
List code / Required listInput | Reference to a list of data to operate on |
Example Payload for Append
{
"data": {
"list": [
1,
2,
3,
4
]
}
}
Chunks
Chunk the list into lists of the specified number of elements | key: chunks
| Input | Default | Notes | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
List code / Required listInput | Reference to a list of data to operate on | ||
Number of Elements string / Required numberInput | 1 | Number of elements to take | 3 |
Example Payload for Chunks
{
"data": [
[
1,
2,
3
],
[
4,
5,
6
],
[
7,
8
]
]
}
Combine Collection (Deprecated)
This version of the action is being deprecated. Please replace action with Create Object. | key: combineCollections
| Input | Notes | Example |
|---|---|---|
Collections string / Required Key Value List collections | Returns an object with the specified key and corresponding collection as the value | [ {"key": "CustomerQueryResult", "value": { Customer: { Name: "Acme Contracting" } }}, {"key": "AccountQueryResult", "value": { Account: { AccountId: "123123123" } }}, ] |
Example Payload for Combine Collection (Deprecated)
{
"data": {
"CustomerQueryResult": {
"Customer": {
"Name": "Acme Contracting"
}
},
"AccountQueryResult": {
"Account": {
"AccountId": "123123123"
}
}
}
}
Concatenate
Concatenate two lists together into a single list | key: concatenate
| Input | Notes | Example |
|---|---|---|
List code / Required anotherListInput | Reference to a list of data to operate on | |
List code / Required listInput | Reference to a list of data to operate on |
Example Payload for Concatenate
{
"data": [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6
]
}
Count
Count the number of occurrences of element in list | key: count
| Input | Notes |
|---|---|
Element data / Required elementInput | Reference to an element to look for |
List code / Required listInput | Reference to a list of data to operate on |
Example Payload for Count
{
"data": 3
}
Create List
Create a new list with the given inputs | key: create
| Input | Notes |
|---|---|
List Items data Value List items |
Example Payload for Create List
{
"data": [
1,
2,
3,
4
]
}
Create Object
Creates a new object from provided key/value pairs | key: createObject
| Input | Notes |
|---|---|
Key & Value Pairs data / Required Key Value List keyValueInput | Key and value pairs |
Example Payload for Create Object
{
"data": {
"first": "value",
"second": 17
}
}
De-duplicate
De-duplicate the elements of the list | key: deduplicate
| Input | Notes |
|---|---|
List code / Required listInput | Reference to a list of data to operate on |
Example Payload for De-duplicate
{
"data": [
1,
2,
3
]
}
Field Value Mapping
Maps the values from two different collections and returns a key/value list where the 'key' is the value of the Key Mappings input and the 'value' is the value of the Value Mappings input | key: fieldValueMapping
| Input | Notes | Example |
|---|---|---|
Key Mappings data mappings | [{"key":"AccountName","value":"Deploy_Time_Specified_Account_Name__c"},{"key":"AccountValue","value":"Deploy_Time_Specified_Account_Value__c"}] | |
Value Mappings string Key Value List values | [{"key":"AccountName","value":"bar"},{"key":"AccountValue","value":"baz"}] |
Example Payload for Field Value Mapping
{
"data": [
{
"key": "Deploy_Time_Specified_Account_Name__c",
"value": "bar"
},
{
"key": "Deploy_Time_Specified_Account_Value__c",
"value": "baz"
}
]
}
Filter
Filter elements of a list | key: filter
| Input | Default | Notes | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
Filter Function code filterCodeInput | Filter out any elements that do not return true | ||
List code / Required listInput | Reference to a list of data to operate on |
This action applies a NodeJS filter function to an array of data.
The filter function should use arrow notation, and include an input (an element) and a function that evaluates to true or false.
Its return value is an array of elements that evaluated to true.
Simple Filter
For example, if you have an array, ["exuberant", "spray", "limit", "elite", "destruction", "present"], and you would like words with a length greater than 6, your filter function could read:
(word) => word.length > 6;
The result would be ["exuberant", "destruction", "present"] - all words whose length is greater than 6.
Filters on Objects
If your array is comprised of objects, you can apply a filter using each object's properties.
For example, suppose you have an array of objects like this:
[
{
"name": "Widget",
"cost": 80,
"available": true
},
{
"name": "Whatsits",
"cost": 90,
"available": false
},
{
"name": "Whoseits",
"cost": 120,
"available": true
},
{
"name": "Whysits",
"cost": 75,
"available": true
}
]
If you want to find items whose cost is less than 100 that have true for availability, you can write a filter function like this:
(item) => item.cost < 100 && item.available;
The return value of this example would be an array of two objects that passed the filter:
[
{
name: "Widget",
cost: 80,
available: true,
},
{
name: "Whysits",
cost: 75,
available: true,
},
];
First
Get first element from a list | key: first
| Input | Notes |
|---|---|
List code / Required listInput | Reference to a list of data to operate on |
Flatten
Flatten an array of arrays into a single array | key: flatten
| Input | Notes | Example |
|---|---|---|
List code / Required listInput | Reference to a list of data to operate on |
Example Payload for Flatten
{
"data": [
1,
2,
[
3,
[
4
]
],
5
]
}
Key Value Pair List to Object
Convert a Key Value list to an Object | key: toObject
| Input | Notes | Example |
|---|---|---|
Key/Value List code / Required kvList |
Example Payload for Key Value Pair List to Object
{
"data": {
"FirstName": "Foo",
"LastName": "Bar"
}
}
Last
Get last element from a list | key: last
| Input | Notes |
|---|---|
List code / Required listInput | Reference to a list of data to operate on |
Length
Count the number of elements in list | key: length
| Input | Notes |
|---|---|
List code / Required listInput | Reference to a list of data to operate on |
Example Payload for Length
{
"data": 7
}
Map
Transform a list and its elements | key: map
| Input | Default | Notes | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
Context Data data contextInput | Additional contextual data to supply to the transform and filter functions | ||
Filter Function code filterCodeInput | Filter out any elements that do not return true | ||
List code / Required listInput | Reference to a list of data to operate on | ||
Transform (map) Function code transformCodeInput | Function to transform each element |
This action applies a NodeJS map function to an array of data.
It also has an optional filter function - see the Filter action for examples. The action applies the filter function (if present), and then the map function to your array.
Simple Map Function
If you have an array of integers that represent pennies, like [1234, 567, 890], and you would like to turn all values in dollar amounts, you could divide all values using a map function like this:
(value) => value / 100;
The result of the step would be an array that reads [12.34, 5.67, 8.9]
Mapping on Objects
If you have an array of objects, you can reference the object's fields in your map function. Suppose you have an array of "people" objects, and you'd like to concatenate their names and order in the list.
Your data might look like this:
[
{ "first": "Bob", "last": "Smith", "middle": "Billy" },
{ "first": "John", "last": "Doe" },
{ "first": "Lisa", "last": "Nguyen", "middle": "Sue" }
]
Your map function could look like this:
(person, index) => {
if (person.middle) {
return `${index} - ${person.last}, ${person.first} ${person.middle[0]}.`;
} else {
return `${index} - ${person.last}, ${person.first}`;
}
};
The result of the step would be an array of strings:
["0 - Smith, Bob B.", "1 - Doe, John", "2 - Nguyen, Lisa S."]
Providing additional context to the map function
You can provide additional context to the map function by using the context input.
context can be anything - a string, number or object.
For example, suppose your data is an array of objects:
[
{ "product": "Item 1", "price": 10 },
{ "product": "Item 2", "price": 11 },
{ "product": "Item 3", "price": 12 },
{ "product": "Item 4", "price": 9 },
{ "product": "Item 5", "price": 15 },
{ "product": "Item 6", "price": 16 }
]
If you provide the context as an object:
{ "minPrice": 10, "prepend": "My" }
And your filter function looks like this:
(item, index, context) => {
return item.price > context.minPrice;
};
And your map function looks like this:
(item, index, context) => {
return `${context.prepend} ${item.product}`;
};
Then your result would be the names of all items with a price greater than 10, with "My " prepended to the name:
["My Item 2", "My Item 3", "My Item 5", "My Item 6"]
Object to Key Value Pair List
Convert an Object to a Key Value List | key: fromObject
| Input | Notes | Example |
|---|---|---|
Object data / Required object | { FirstName: "Foo", LastName: "Bar" } |
Process In Order
Ensures that payloads are processed in order across executions according to an ordering specified by a payload attribute. Returns the largest possible set of ordered payloads on the Process branch, and otherwise follows the Skip branch and returns the current item. | key: processInOrder
| Input | Notes | Example |
|---|---|---|
Collection ID string / Required collectionId | A value that uniquely identifies the collection that is being processed out of order. | da41e39f-ea4d-435a-b922-c6aae3915ebe |
Collection Length data / Required collectionLength | The number of items in the collection. When processing is finished the interim data for the collection is removed. | 100 |
Item data / Required item | The current item to consider for processing. | { Index: 0, Name: "Acme Contracting" } |
Item Index data / Required itemIndex | The integer value to consider as the index for the current item that specifies intended processing order. 0 is the first index value. | 10 |
The Process In Order action allows you to send several requests to an instance out of order, and helps to ensure that data runs through your integration in order. Requests with data payloads are collected, and when an ordered set of requests have been received this action processes the requests in the order you specify.
In order to use this action, you will need to know how many total items you are sending ahead of time.
Example: suppose we are updating an inventory system with three updates, and order is important. We want to process widgets first, then gadgets, and finally whatsits. We know that we have three items to import, and due to limitations of our third-party system we can't send them all at once. We're not confident that they'll arrive to Prismatic in any particular order, so we'll use this action to help.
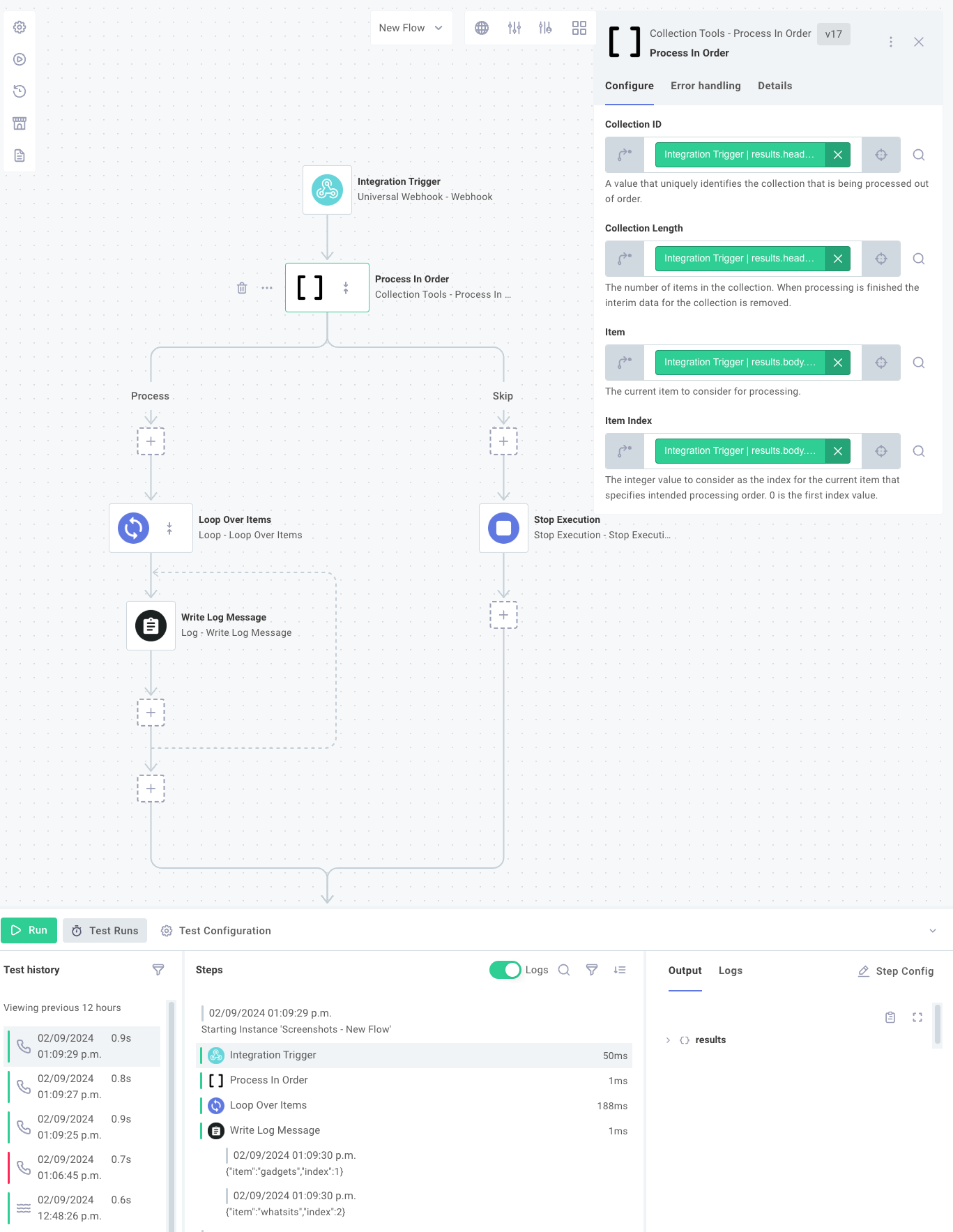
We'll come up with a unique "Collection ID", and begin sending our data in any order:
$ curl 'https://hooks.prismatic.io/trigger/EXAMPLE==' \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data '{"item": "whatsits", "index": 2}' \
--header 'collectionid: abc-123' \
--header 'collectionlength: 3'
$ curl 'https://hooks.prismatic.io/trigger/EXAMPLE==' \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data '{"item": "widgets", "index": 0}' \
--header 'collectionid: abc-123' \
--header 'collectionlength: 3'
$ curl 'https://hooks.prismatic.io/trigger/EXAMPLE==' \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data '{"item": "gadgets", "index": 1}' \
--header 'collectionid: abc-123' \
--header 'collectionlength: 3'
The first time that our integration is invoked, the {"item": "whatsits", "index": 2} payload will be stored for future processing, since items with index 0 and 1 have not yet been processed.
The second time that our integration is invoked, the {"item": "widgets", "index": 0} payload will be processed immediately, since it has index 0, but then our loop will stop since an item with index 1 has not yet been received.
The third time our integration is invoked, the {"item": "gadgets", "index": 1} will be processed right away, since it has index 1 and an item with index 0 has already been processed.
The {"item": "whatsits", "index": 2} payload will also be pulled from storage and processed since it is next in line to be processed.
At this point all items will have been processed.
Note: Items must be zero-indexed.
Example Payload for Process In Order
{
"data": [
{
"Index": 0,
"Name": "Acme Contracting"
},
{
"Index": 1,
"Name": "FooBar Consulting"
}
],
"instanceState": {
"7d577253-3ef0-4a0a-bb7f-8335c2596e70": {
"da41e39f-ea4d-435a-b922-c6aae3915ebe": {
"lastIndex": 1,
"items": []
}
}
},
"branch": "Process"
}
Remove
Remove all occurrences of an element from a list | key: remove
| Input | Notes |
|---|---|
Element data / Required elementInput | Reference to an element to look for |
List code / Required listInput | Reference to a list of data to operate on |
Example Payload for Remove
{
"data": [
1,
3
]
}
Select Item From List by Index
Select an item by index from a list of items, supports nested lists | key: selectItemFromList
| Input | Notes |
|---|---|
Index data / Required Value List indexInput | |
List code / Required listInput | Reference to a list of data to operate on |
Example Payload for Select Item From List by Index
{
"data": [
1,
2,
3,
4
]
}
Sort
Sort elements using a JavaScript comparison function | key: sort
| Input | Default | Notes |
|---|---|---|
List code / Required list | Reference to a list of data to operate on | |
Sort Comparison Function code sortComparisonFunction | Sort elements by the given comparison function. See https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/sort for compare function documentation. |
Take First
Take first number of elements from a list | key: takeFirst
| Input | Default | Notes | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
List code / Required listInput | Reference to a list of data to operate on | ||
Number of Elements string / Required numberInput | 1 | Number of elements to take | 3 |
Example Payload for Take First
{
"data": [
1,
2,
3
]
}
Take Last
Take last number of elements from a list | key: takeLast
| Input | Default | Notes | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
List code / Required listInput | Reference to a list of data to operate on | ||
Number of Elements string / Required numberInput | 1 | Number of elements to take | 3 |
Example Payload for Take Last
{
"data": [
7,
8,
9
]
}
Validate JSON Schema
Validate a JSON input against a given schema, returning errors if not JSON input is not valid. | key: validateJsonSchema
| Input | Default | Notes |
|---|---|---|
JSON Object code / Required jsonInput | The JSON object to validate against the schema. | |
JSON Schema code / Required jsonSchema | The JSON schema to validate the input against. |
Validate XML Schema
Validate an XML input against a given XSD schema, returning errors if XML is not valid. | key: validateXmlSchema
| Input | Notes |
|---|---|
XML code / Required xmlInput | The XML object to validate against the schema. |
XML Schema code / Required xmlSchema | The XSD schema to use in validation. |