Salesforce Field Mapper
Every customer of Salesforce (SFDC) configures their account differently. Some Salesforce customers add unique fields to existing resources. Others use existing fields in unique ways.
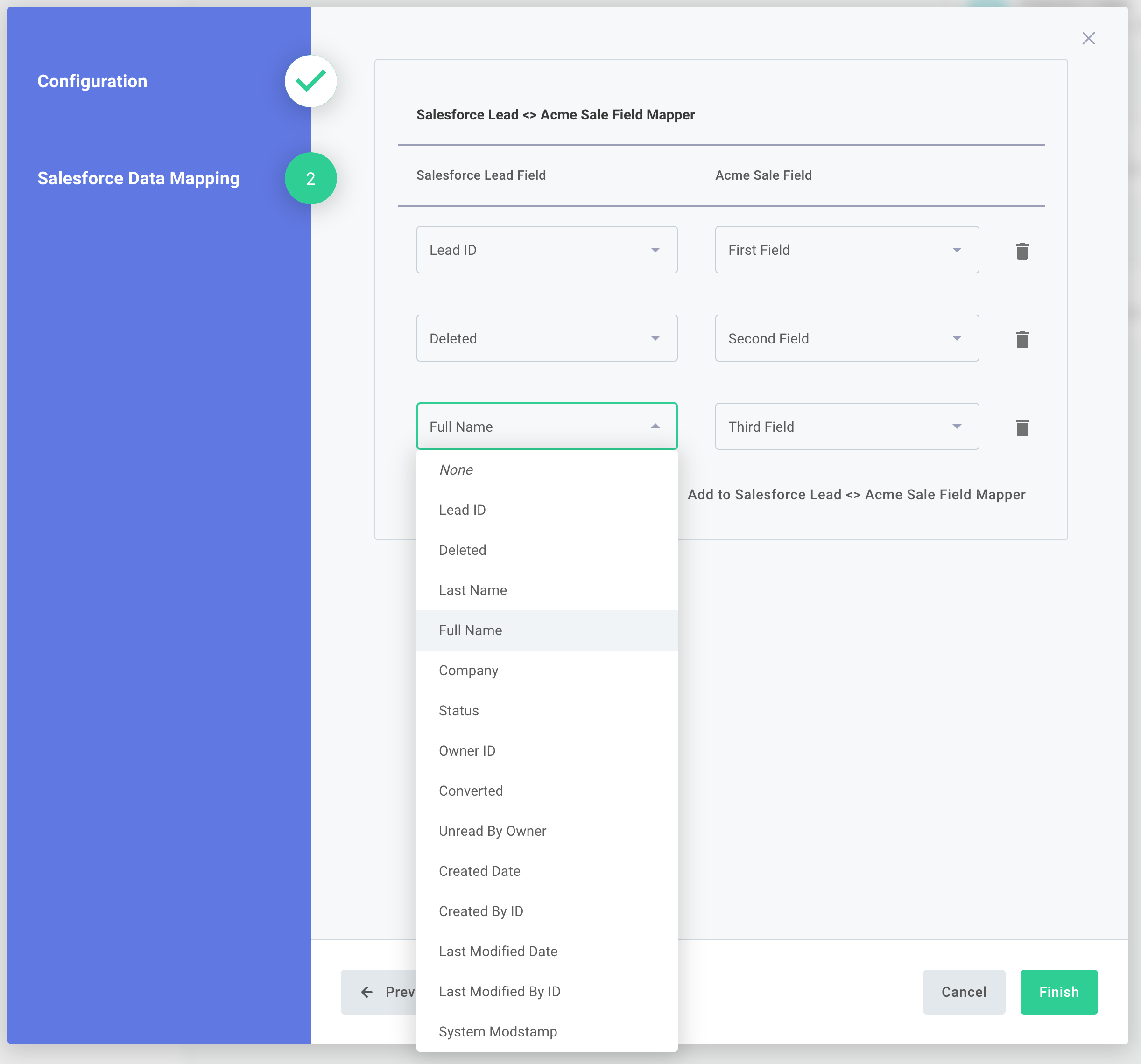
If you integrate with a CRM like SFDC, you may want your users to map fields from the CRM to your product. In this tutorial, you'll learn how to use an existing Salesforce connection to fetch your customer's SFDC fields and present them to a user as a field map during the instance configuration process using JSON Forms.
The final product is available in our examples repo.
Initializing the data source component
You can initialize the data mapper data source project as you would any other custom component.
After initializing the component, remove all templated files in the src/ directory.
Then, install Salesforce's NPM package, jsforce:
npm install jsforce
npm install --save-dev @types/jsforce
If you are integrating with a different CRM, you can use their respective NPM package or a generic HTTP client.
Reusing HTTP connections
It would be a poor user experience to require a user to authenticate with Salesforce twice. Instead, add a Salesforce step to your integration (that will automatically create a Salesforce connection config variable). You can re-use that existing Salesforce connection for your data source!
You do not need to define any connections for your component.
Simply add a connection input to your data source:
const salesforceFieldMappingExample = dataSource({
dataSourceType: "jsonForm",
display: {
label: "Salesforce field mapping example",
description: "Map fields from a Salesforce 'Lead' to an acme 'Sale'",
},
inputs: {
sfConnection: input({
label: "Salesforce Connection",
type: "connection",
required: true,
}),
},
// ...
});
The Salesforce connection uses OAuth, so the access token that you'll need will be available via sfConnection.token?.access_token.
Fetch fields from SFDC
Next, you'll use the existing connection to fetch fields from SFDC.
{
// ...
perform: async (context, params) => {
// Reference an existing SFDC OAuth access token
const salesforceClient = new jsforce.Connection({
instanceUrl: util.types.toString(params.sfConnection.token?.instance_url),
version: "63.0",
accessToken: util.types.toString(params.sfConnection.token?.access_token),
});
// Fetch all fields on a Lead using https://jsforce.github.io/document/#describe
const { fields } = await salesforceClient.sobject("Lead").describe();
// Filter out non-required fields
const salesforceRequiredLeadFields = fields.filter(
({ nillable }) => !nillable,
);
};
}
For illustration purposes, this example fetches fields on the "Lead" resource and filters them down to only fields that are required (i.e. not nillable).
You can fetch fields on any resource and can choose to filter those fields or not.
Generate a JSON Forms schema
JSON Forms allows you to define a schema where you declare how the UI that your customer uses should look. Here, this example hard-codes some fields from "Acme" and creates an array where every element of the array has one Salesforce Lead field and one Acme field:
// Hard-code Acme fields - these can be fetched from an external source, too
const acmeSaleFields: { name: string; id: number }[] = [
{ id: 123, name: "First Field" },
{ id: 456, name: "Second Field" },
{ id: 789, name: "Third Field" },
];
// Schema defines the shape of the object to be returned to the integration,
// along with options for dropdown menus
const schema = {
type: "object",
properties: {
mymappings: {
// Arrays allow users to make one or more mappings
type: "array",
items: {
// Each object in the array should contain a salesforceField and an acmeField
type: "object",
properties: {
salesforceLeadField: {
type: "string",
// Have users select "one of" a dropdown of items
oneOf: salesforceRequiredLeadFields.map((field) => ({
// Display the pretty "label" like "My First Name" to the user
title: field.label,
// Feed programmatic "name" like "My_First_Name__c" to the integration
const: field.name,
})),
},
acmeSaleField: {
type: "string",
oneOf: acmeSaleFields.map((field) => ({
title: field.name,
const: util.types.toString(field.id), // JSON Forms requires string values
})),
},
},
},
},
},
};
JSON Forms also require UI schema, which determines how the above UI elements should be placed (vertically, horizontally, etc):
// UI Schema defines how the schema should be displayed in the configuration wizard
const uiSchema = {
type: "VerticalLayout",
elements: [
{
type: "Control",
scope: "#/properties/mymappings",
label: "Salesforce Lead <> Acme Sale Field Mapper",
},
],
};
Add an optional default mapping
If you have an idea of what SFDC fields should map to your fields, you can provide a default mapping. Here, for illustration purposes, this example simply maps the first three SFDC fields to the three Acme fields:
const defaultValues = {
mymappings: [
{
salesforceLeadField: util.types.toString(
salesforceRequiredLeadFields[0].name,
),
acmeSaleField: util.types.toString(acmeSaleFields[0].id),
},
{
salesforceLeadField: util.types.toString(
salesforceRequiredLeadFields[1].name,
),
acmeSaleField: util.types.toString(acmeSaleFields[1].id),
},
{
salesforceLeadField: util.types.toString(
salesforceRequiredLeadFields[2].name,
),
acmeSaleField: util.types.toString(acmeSaleFields[2].id),
},
],
};
return {
result: { schema, uiSchema, data: defaultValues },
};
AI-enhanced field mapping
You can enhance your field mapper with AI to automatically generate intelligent field mappings. This uses OpenAI to analyze field names and suggest semantic matches between Salesforce fields and your destination fields, pre-populating the mapping form for faster configuration.
Learn how to implement AI-enhanced field mapping →
The completed code
The full source code of this field mapper can be found in our examples repo. It serves as a good jumping-off point for your own field mapping, and you can modify it however you like. For example you could:
- Fetch your app's fields dynamically rather than hard-coding them
- Fetch fields for other SFDC resources, like opportunities or accounts
- Fetch fields from another CRM
Using the field mapper data in an integration
The next step is to use the results of that field mapper to map data in a flow.
In the video above, you create a field mapper that maps Salesforce fields to "Acme" fields. The result of the field mapper config variable is a JavaScript object that looks like this:
[
{
"source": "Id",
"destination": "external_id",
},
{
"source": "Name",
"destination": "acct_name",
},
{
"source": "AnnualRevenue",
"destination": "revenue",
},
];
Salesforce yields data that looks like this, with keys in Pascal Case:
{
"Id": "0018c0000321QvpAAE",
"Name": "Example Account",
"AnnualRevenue": 1000000
}
To map fields from the Salesforce payload to an "Acme" payload, you can apply a JavaScript reduce function onto the map configuration object:
module.exports = async ({ logger, configVars }, stepResults) => {
const sfdcAccount = stepResults.loopOverAccounts.currentItem;
const mapping = configVars["Salesforce Account Field Mapping"];
const mappedFields = mapping.reduce(
(acc, { source, destination }) => ({
[destination]: sfdcAccount[source],
...acc,
}),
{},
);
return { data: mappedFields };
};
That will yield an object that our "Acme" API can consume:
{
"external_id": "0018c0000321QvpAAE",
"acct_name": "Taylor test account 5",
"revenue": 10000
}