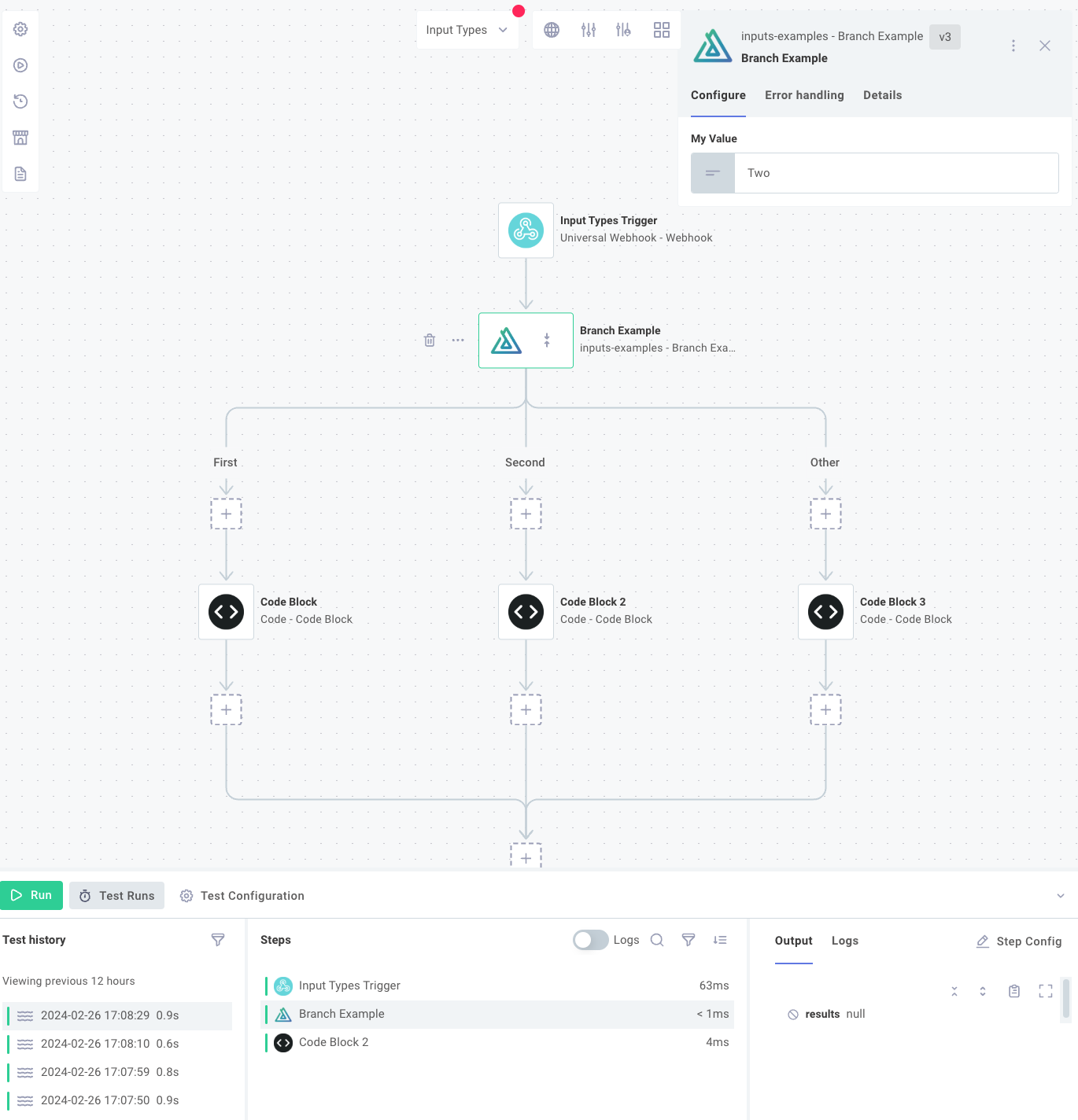
Branching in Custom Actions and Triggers
Similar to the branch component, your custom actions and triggers can make use of logical branches.
To support branches, give your action() or trigger() two additional properties, allowsBranching: true and staticBranchNames: ["List", "Of", "Branches"], and ensure that the object that your perform function returns includes a branch property:
Example action with branching
export const branchExample = action({
display: {
label: "Branch Example",
description: "An example action that branches",
},
inputs: {
myValue: input({ label: "My Value", type: "string", required: true }),
},
allowsBranching: true,
staticBranchNames: ["First", "Second", "Other"],
perform: async (context, params) => {
let branchName = "Other";
if (params.myValue === "One") {
branchName = "First";
} else if (params.myValue === "Two") {
branchName = "Second";
}
return await Promise.resolve({ branch: branchName, data: null });
},
});
Similar code can be used in a custom trigger.
allowsBranching: true indicates to the integration designer that it should render branches beneath your action or trigger.
staticBranchNames is an array of strings representing names of possible branches that can be followed.
The branch name that matches the branch return value will be followed.