MCP Flow Server
MCP is an open protocol, introduced by Anthropic, that standardizes how LLMs request context from applications. When an LLM connects to an MCP server, it requests a list of tools that the MCP server offers.
These tools can perform actions such as "Find people with a specified name in HubSpot" or "Add an event to my Google Calendar." An MCP server offers a standardized schema so LLMs know to send a first and last name to the "find people" tool or an event name and date to the "add event" tool.
How does Prismatic's MCP Flow Server work?
In the Prismatic MCP Flow Server, the tools are implemented as agent flows. You can use agent flows as your tools to add validation and better error handling using either the low-code designer or the full power of code-native integrations.
Prismatic offers a built-in MCP flow server which allows you to connect to all of your agent flows. This will be the best supported approach to interact with the Prismatic platform via MCP, but if you have specific use cases you can opt to build your own MCP server and still interact with your Prismatic agent flows.
Before connecting Prismatic's MCP flow server (or before building your own), ensure that you've created agent flows that have invocation schema, so your LLM has something to query.
When querying for agent flows as an organization team member, you will receive a list of agent flows within your test instances (the instances you interact with in the integration designer). You will not see your customers' instances' agent flows.
Customer users, on the other hand, will see agent flows of production instances deployed to their customer.
Prismatic's MCP flow server
Prismatic offers a hosted MCP flow server that can be used to connect to your agent flows. Below are MCP endpoints for Prismatic's public regions. If your organization uses private stack, please contact support for your MCP endpoint.
| Region | MCP Endpoint |
|---|---|
| US Commercial (default) | mcp.prismatic.io/mcp |
| US GovCloud | mcp.us-gov-west-1.prismatic.io/mcp |
| Europe (Ireland) | mcp.eu-west-1.prismatic.io/mcp |
| Europe (London) | mcp.eu-west-2.prismatic.io/mcp |
| Canada (Central) | mcp.ca-central-1.prismatic.io/mcp |
| Australia (Sydney) | mcp.ap-southeast-2.prismatic.io/mcp |
| Africa (Cape Town) | mcp.af-south-1.prismatic.io/mcp |
| Private Stack | mcp.<your-prismatic-domain>/mcp |
These global MCP endpoints will provide your AI agent with access to all agent flows.
If you would like the MCP server to return only the agent flows for a specific integration, open the MCP tab of your integration and take note of the custom MCP endpoint.
It will look like https://mcp.prismatic.io/SW5...../mcp.
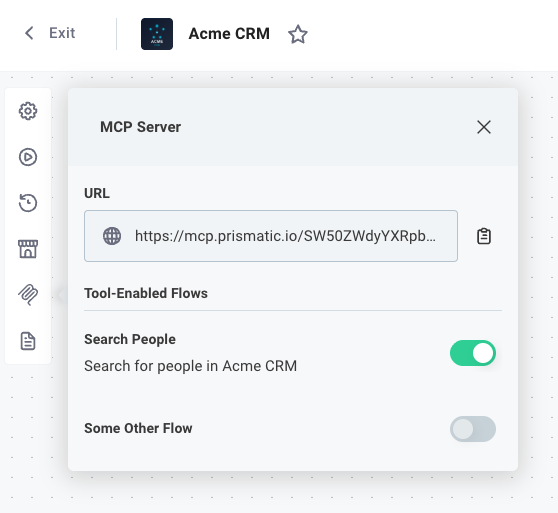
Connecting an MCP Client to Prismatic's MCP flow server
See Connecting AI Agents for more details on how to connect an AI agent (like Claude, OpenAI, Cursor or other agents) to Prismatic's MCP flow server.
Building your own MCP flow server using Prismatic flows
If you would like to build your own MCP flow server and instruct it to interact with agent flows in Prismatic, your MCP flow server must be told which flows are available to be queried. This example code instructs an MCP flow server to fetch agent flows from Prismatic's API, and creates a resource for each:
import {
type JSONSchema,
JSONSchemaToZod,
} from "@dmitryrechkin/json-schema-to-zod";
import {
McpServer,
type ToolCallback,
} from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/mcp.js";
import { gql, request } from "graphql-request";
const STACK_BASE_URL = "https://app.prismatic.io"; // Change this to your own region
const PRISMATIC_API_KEY = ""; // TODO: Set your Prismatic API key here
interface AgentFlowResponse {
ai: {
agentFlows: {
nodes: {
id: string;
name: string;
description: string;
webhookUrl: string;
apiKeys: string[];
invokeSchema: string;
resultSchema: string;
}[];
};
};
}
// Query for agentFlows
const result = await request<AgentFlowResponse>(
new URL("/api", STACK_BASE_URL).toString(),
gql`
query agentFlows {
ai {
agentFlows {
nodes {
id
name
description
webhookUrl
apiKeys
invokeSchema
resultSchema
}
}
}
}
`,
{},
{
Authorization: `Bearer ${PRISMATIC_API_KEY}`,
},
);
// Customize MCP server to allow custom tool registrations, particularly
// for use with JSON Schema (as, by default, only zod schemas are supported).
class DynamicMcpServer extends McpServer {
jsonSchemaTool(
name: string,
description: string,
schema: JSONSchema,
cb: ToolCallback,
): void {
const zodSchema = JSONSchemaToZod.convert(schema) as any;
super.tool(name, description, zodSchema.shape, cb);
}
}
const server = new DynamicMcpServer({
name: "person-getter",
version: "1.0.0",
capabilities: {
resources: {},
tools: {},
},
});
// For each flow, create a tool that can be invoked by the MCP client
for (const flow of result.ai.agentFlows.nodes) {
server.jsonSchemaTool(
flow.name,
flow.description,
JSON.parse(flow.invokeSchema),
async (args) => {
console.log("flow invoke", flow.name, args);
const result = await fetch(flow.webhookUrl, {
method: "POST",
body: JSON.stringify(args),
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"prismatic-synchronous": "true",
},
});
return { content: [{ type: "text", text: await result.text() }] };
},
);
}